
What Is QQQ: An Essential Guide to the Nasdaq 100 ETF
At its core, the Invesco QQQ Trust (ticker symbol QQQ) is a hugely popular Exchange-Traded Fund, or ETF. Think of it as a single investment that gives you a piece of the 100 largest, most innovative non-financial companies listed on the Nasdaq stock market.
It's a straightforward way to buy into tech and growth powerhouses like Apple, Microsoft, and NVIDIA without the hassle and cost of purchasing each company's stock individually. One click, and you're in.
Decoding the QQQ ETF
So, what does that really mean for an investor? Imagine you wanted to own all the biggest and best-known tech and growth stocks. Buying them one by one would be a massive undertaking. QQQ bundles them up for you.
This "bundle" is designed to mirror the performance of a specific stock market index: the Nasdaq-100 Index. This is a critical point. The Nasdaq-100 specifically leaves out financial companies like big banks and insurance firms, which is why QQQ has such a strong focus on technology and innovation.
What Does QQQ Stand For?
Funny enough, the ticker "QQQ" doesn't actually stand for anything. It's just the stock symbol the fund was given when it first launched. But over the years, that simple, memorable ticker has become iconic—it's now practically synonymous with investing in the Nasdaq's top growth companies.
QQQ first hit the market on March 10, 1999, right in the middle of the dot-com boom, and it quickly became a go-to for investors. Today, it’s one of the largest and most-traded ETFs in the world. Its performance has been remarkable, delivering a total cumulative return of 839.54% from its launch through the end of 2023. For comparison, the S&P 500 returned 489.24% over that same stretch. For more recent performance data, you can always check the official Invesco site for their detailed quarterly outlook.
Let's quickly break down the essentials of what makes QQQ tick. This table gives you a scannable overview of its main characteristics.
QQQ at a Glance: Key Characteristics
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Ticker Symbol | QQQ |
| Underlying Index | Nasdaq-100 Index |
| Asset Class | U.S. Large-Cap Growth Equity |
| Number of Holdings | 101 (The Nasdaq-100 includes 101 securities from 100 companies) |
| Expense Ratio | 0.20% |
| Inception Date | March 10, 1999 |
| Primary Sector Exposure | Information Technology |
| Trading | Trades like a stock on the Nasdaq exchange |
This snapshot helps you see why QQQ is a favorite: it's a simple, targeted, and cost-effective way to access a specific slice of the market.
Is QQQ an ETF or an Index Fund?
This is a great question and a common source of confusion. The short answer is that QQQ is an Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF).
It behaves a lot like an index fund because its whole job is to track an index—the Nasdaq-100. But how it's bought and sold is what makes it an ETF.
Key Difference: You can buy and sell shares of QQQ throughout the day on the stock exchange, just like you would with a share of Apple or Amazon. Its price moves up and down with the market. Traditional index mutual funds are different; they are priced just once at the end of the trading day.
This ability to trade in real-time is a huge part of the appeal of ETFs like QQQ, making them popular with everyone from long-term, buy-and-hold investors to more active traders.
What's Really Inside the QQQ ETF?
To get a real feel for QQQ, you have to pop the hood and look at its engine: the Nasdaq-100 Index. This isn't just a random grab-bag of stocks. It’s a handpicked list of the 100 biggest and most influential non-financial companies trading on the Nasdaq.
The index has some ground rules for which companies get in, mostly based on size and how often their shares trade. But the one rule that truly defines QQQ is its strict "no financials" policy. This deliberate choice is what gives the fund its famous tech-heavy personality and sets it apart from your typical broad-market ETF.
The Power Players: QQQ's Top Holdings
Because the Nasdaq-100 is weighted by market capitalization, the biggest companies have the most muscle. This means that a small handful of household names are really steering the ship, and their performance has a massive impact on the entire fund.
A quick glance at the top holdings reads like a who's who of modern innovation:
- Microsoft Corp (MSFT): The undisputed king of software, a cloud computing giant with Azure, and a major force in AI.
- Apple Inc (AAPL): Dominates our pockets and desks with the iPhone and Mac, all while building a massive services empire.
- NVIDIA Corp (NVDA): The brains behind the AI boom, designing the graphics processing units (GPUs) that power it all.
- Amazon.com Inc (AMZN): A global juggernaut in just about everything—from e-commerce and cloud services (AWS) to streaming.
- Broadcom Inc (AVGO): A critical supplier of the semiconductors and software that form the backbone of our connected world.
- Meta Platforms Inc (META): The parent company of Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp, shaping social media and betting big on the metaverse.
- Costco Wholesale Corp (COST): The retail giant that proves a simple membership model can build an incredibly loyal customer base.
- Tesla Inc (TSLA): Pushing the boundaries of what's possible with electric vehicles, battery storage, and self-driving tech.
- Alphabet Inc (GOOG/GOOGL): The company behind Google, a behemoth in search, online advertising, and countless other tech ventures.
- Netflix Inc (NFLX): The original streaming disruptor that changed how the world watches movies and TV shows.
These top ten companies alone make up a huge chunk of the entire fund. That concentration is a classic double-edged sword. When these titans are winning, QQQ absolutely flies. But if just a few of them stumble, they can drag the whole ETF down with them.
A Look at Sector Exposure
While everyone calls QQQ a "tech fund," its investments are actually spread across a few key areas of the economy. Understanding this breakdown shows you exactly where your money is going.
The chart below gives you a powerful visual of QQQ's long-term growth, which has been fueled by this specific mix of sectors. You can see how dramatically it has outpaced the broader S&P 500 over the years.
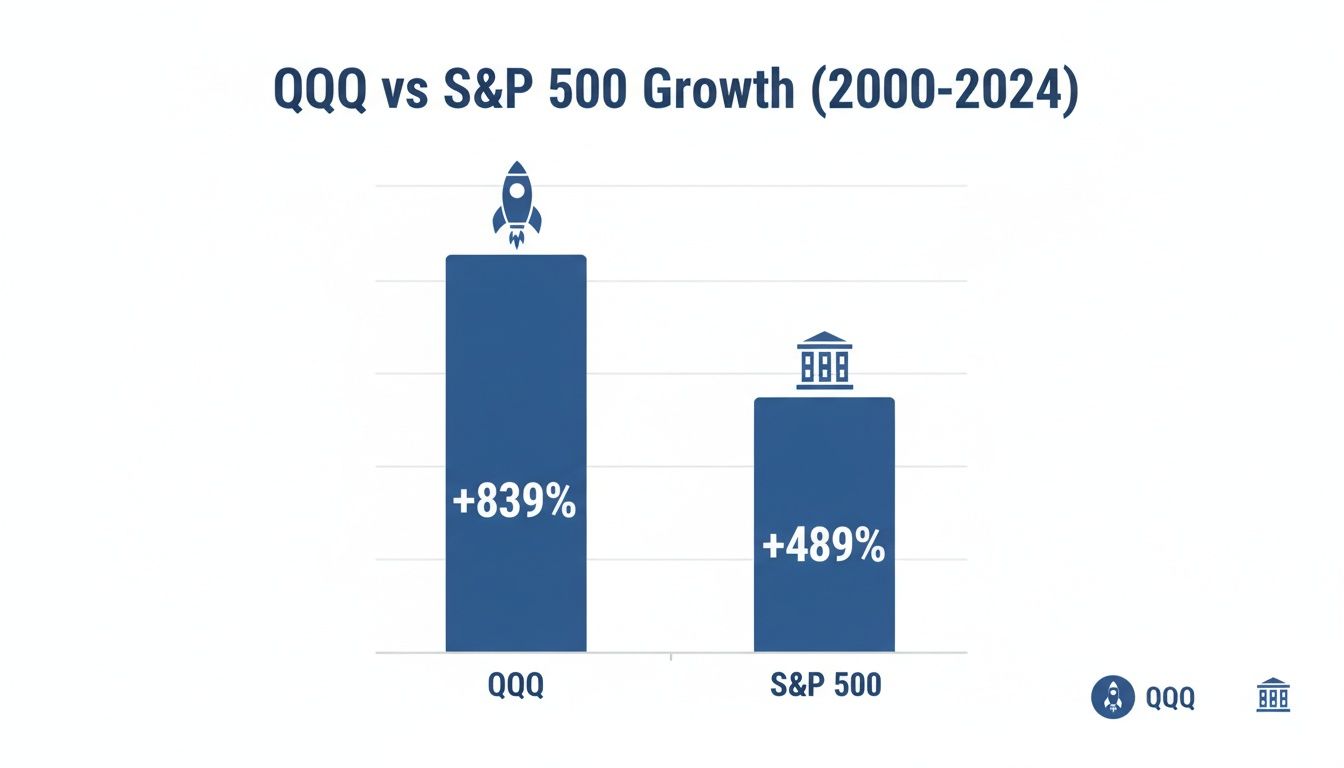
The data doesn't lie. QQQ's focus on innovative, high-growth companies has historically delivered returns that have left the more diversified S&P 500 in the dust.
So, what's the recipe for that performance? Here’s the sector breakdown:
| Sector | Approximate Weighting |
|---|---|
| Information Technology | ~58% |
| Communication Services | ~16% |
| Consumer Discretionary | ~12% |
| Health Care | ~6% |
| Consumer Staples | ~5% |
| Industrials | ~2% |
| Other | ~1% |
With nearly 60% of its money in Information Technology, it’s impossible to ignore that buying QQQ is a major bet on the future of tech. That makes it a fantastic tool if you want to add more tech exposure to your portfolio, but it also shines a spotlight on the concentration risk you're taking on. If you're looking to diversify, check out our guide on the top stocks for smart investors.
Real-Life Example: Think about it this way. Imagine NVIDIA reports earnings that blow past expectations due to soaring demand for their AI chips. Their stock might jump 10% in a single day. Because NVIDIA is a heavyweight in the QQQ, that single piece of good news will directly and noticeably lift the value of the entire ETF, even if dozens of smaller companies in the fund are having a flat day. This is concentration in action.
Comparing QQQ vs SPY for Your Portfolio
When you talk about the big-hitter ETFs, two names always come up: QQQ and the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY). They're both giants in the investing world, but they offer two completely different ways to own a piece of the U.S. stock market. The right one for you really boils down to your goals, how much risk you're comfortable with, and where you think the market is headed.
Think of SPY as a snapshot of the entire American economy. It’s built to mirror the S&P 500 index, giving you a tiny sliver of 500 of the biggest, most established companies across every industry imaginable—from healthcare and banking to energy and retail. It’s diversification in a can.
QQQ, on the other hand, is a much more focused bet. It follows the Nasdaq-100, which means it zeroes in on the 100 largest non-financial companies on the Nasdaq exchange. This makes it heavy on technology and innovation, designed for investors who want direct exposure to the companies building tomorrow.

QQQ vs SPY: A Head-to-Head Comparison
To really get a feel for how different they are, it helps to put them side-by-side. The table below breaks down the key distinctions that give each ETF its unique personality.
| Metric | Invesco QQQ (QQQ) | SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY) |
|---|---|---|
| Underlying Index | Nasdaq-100 | S&P 500 |
| Number of Holdings | 101 | 503 |
| Top Sector | Information Technology (~58%) | Information Technology (~30%) |
| Diversification | Low (Concentrated in tech/growth) | High (Covers all 11 GICS sectors) |
| Investment Focus | Growth and Innovation | Broad Market/Value and Growth |
| Expense Ratio | 0.20% | 0.09% |
| Best For | Investors seeking higher growth potential. | Investors seeking broad diversification and stability. |
As you can see, the differences are huge. SPY gives you that broad, steady exposure with over 500 stocks, while QQQ puts most of its eggs in the tech and growth basket. This is why many people see SPY as a foundational piece of a long-term portfolio. To get a better handle on this cornerstone index, you can learn more about investing in the S&P 500 index here.
Performance: The $1,000 Test
So, how do these different investment philosophies play out in the real world? Let's run a simple thought experiment.
Imagine you invested $1,000 into both QQQ and an S&P 500 fund like SPY exactly ten years ago and didn't touch it. What would it be worth today?
This table illustrates the power of compounding and sector focus over the last decade.
| Investment | Initial Amount | Value After 10 Years (Approx.) | Total Return |
|---|---|---|---|
| Invesco QQQ Trust (QQQ) | $1,000 | $4,800 | +380% |
| S&P 500 Fund (e.g., SPY) | $1,000 | $3,200 | +220% |
Note: Returns are approximate as of mid-2024 and include reinvested dividends.
QQQ’s focused bet on innovation clearly paid off handsomely over this period. But it's absolutely critical to remember that those higher returns came with more gut-wrenching ups and downs along the way. Past performance is no crystal ball, but this example really drives home the trade-off between the two funds.
Choosing Your Strategy
Ultimately, picking between QQQ and SPY is all about what fits your plan.
If you’re a younger investor with decades ahead of you and a stomach for volatility, QQQ’s growth potential can be incredibly attractive. It can act as a high-octane growth engine for your portfolio.
On the flip side, if stability and a solid, diversified foundation are your top priorities, SPY is a classic for a reason. It gives you a piece of the whole U.S. economy, which helps cushion the blow if one particular sector hits a rough patch. Many experienced investors don't even choose—they use both, building a core with SPY and adding a dose of QQQ for a dedicated growth "tilt."
And for anyone interested in using these ETFs for more than just buy-and-hold, A Definitive QQQ vs SPY Swing Trading Comparison offers a great deep dive into how they behave in shorter timeframes.
Investing in QQQ: A Step-by-Step Guide
Alright, let's move from theory to practice. The great news is that buying shares of the QQQ ETF is incredibly simple—it’s just like buying a share of Apple or Microsoft. Here’s how you can add this powerhouse fund to your own portfolio.
Before you can buy anything, you need a place to do it. That place is a brokerage account. Think of it as a specialized account that lets you buy and sell investments like stocks and ETFs.
If you're brand new to this, our complete guide on how to start investing in the stock market for beginners is the perfect starting point.
Opening and Funding Your Account
First things first: you need to pick a brokerage. There are tons of great options out there, from established names like Fidelity, Charles Schwab, and Vanguard to newer platforms like Robinhood. Most now offer commission-free trading, which is a huge plus.
Once you’ve picked one and opened your account, you need to add some money. This is usually as simple as linking your bank account and making an electronic transfer. The funds should be ready to invest within a few business days.
How to Buy QQQ in Canada
For my fellow investors up north, the process is nearly identical, but with one extra step to keep in mind: currency. You'll need an account with a Canadian brokerage that lets you trade on U.S. markets, like Questrade, Wealthsimple Trade, or the investing arms of the big banks (RBC, TD, etc.).
Since QQQ is priced in U.S. dollars (USD), your brokerage will convert your Canadian dollars (CAD) for you when you buy. Just be sure to check the exchange rate and any fees they might charge for the conversion. Some platforms also offer USD accounts to help manage this.
Placing Your First QQQ Trade
With a funded account, you’re ready for the exciting part. QQQ is an ETF, which means it trades like a stock all day long. This is different from a traditional mutual fund, which only gets priced once at the end of the day.
Here’s the simple rundown:
- Log in to your brokerage platform.
- Find the Ticker: Just type QQQ into the search bar.
- Set Your Order: You can place a "market order" to buy at whatever the current price is, or a "limit order" to set a specific price you're willing to pay.
- Enter the Amount: Tell the system how many shares you want or the total dollar amount you'd like to invest.
- Confirm the Trade: Give everything a final look to make sure it's correct, then hit the "buy" button.
And that's it! Once the order goes through, you officially own a piece of 100 of the most innovative companies on the planet.
For those interested in more advanced strategies, you can even use your QQQ shares to generate regular cash flow. A popular method for this is selling covered calls for income.
Balancing the Risks and Rewards of QQQ
Every investment is a balancing act, and QQQ is a classic case of high-octane growth potential meeting significant risk. It's crucial to get your head around this trade-off before deciding if this ETF fits into your financial picture. The rewards can be huge, but they don't come for free.
The Allure of High Growth
Let's be clear: the main reason people flock to QQQ is its potential for serious growth. The fund is basically a direct pipeline to the most innovative and powerful companies on the planet. These are the names driving everything from artificial intelligence to cloud computing, and their incredible success has historically translated into massive returns for investors.
The numbers back it up. By December 2023, QQQ had ballooned into the fifth-largest ETF in the world. Today, it’s the second most-traded U.S. ETF based on average daily volume, meaning you can get in and out with ease.
This isn't just a recent trend, either. Its long-term performance has earned it top marks, placing it in the top 1% of its category for 15-year returns according to Lipper. It also boasts a 5-star rating from Morningstar for its 10-year risk-adjusted performance. If you're curious, Invesco provides a fascinating 25-year performance chart of QQQ that shows its journey.
Understanding the Inherent Risks
Here's the flip side. The very thing that powers QQQ’s impressive growth—its concentration—is also its biggest vulnerability. With nearly 60% of its money tied up in the Information Technology sector, QQQ is anything but a diversified bet.
This creates two major risks you need to be aware of:
- Concentration Risk: If the tech sector stumbles, QQQ is going to feel it much harder than a broader fund like an S&P 500 ETF. A single bad headline for a tech giant can send ripples—or even waves—across the entire fund.
- Volatility Risk: The growth-focused companies in QQQ are naturally more volatile than the steady, value-oriented stocks you'd find elsewhere. This means its price can swing wildly, both up and down. You have to be ready for the ride.
A Lesson from History: The dot-com bubble in the late '90s is the ultimate cautionary tale. When that bubble burst in 2000-2002, the Nasdaq-100 index lost nearly 80% of its value. Investors who were over-concentrated in tech saw their portfolios get decimated, highlighting just how dangerous it is to put all your eggs in one sector's basket.
Why Some Experts Urge Caution
You'll often hear financial advisors like Dave Ramsey warn against piling too much cash into a single, concentrated investment. Their advice isn't that QQQ is a "bad" fund. It's a reminder not to forget the golden rule of investing: diversification.
The worry is that leaning too heavily on one sector exposes your portfolio to risks you don't need to take. If your retirement dreams are pinned on the success of just a handful of tech companies, a downturn in that industry could be devastating. That's why it's so important to learn how to diversify your portfolio to build a more resilient financial future.
Ultimately, how much QQQ is right for you boils down to your personal risk tolerance, your investment timeline, and your overall strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions About QQQ (FAQ)
1. What does QQQ stand for?
QQQ doesn't actually stand for anything. It is the ticker symbol assigned to the Invesco QQQ Trust ETF when it launched. It has since become an iconic and recognizable symbol for investing in the Nasdaq-100.
2. What is the difference between QQQ and S&P 500?
The main difference is focus. QQQ tracks the Nasdaq-100, concentrating on the 100 largest non-financial companies, making it heavily weighted towards technology and growth. The S&P 500 (tracked by ETFs like SPY or VOO) is much broader, covering 500 large companies across all sectors of the U.S. economy, offering greater diversification.
3. What if I invested $1,000 in QQQ 10 years ago?
If you had invested $1,000 in QQQ ten years ago and reinvested all dividends, your investment would be worth approximately $4,800 today. This represents a total return of about 380%, showcasing the strong performance of the tech-heavy Nasdaq-100 over the past decade.
4. Is QQQ an ETF or an index fund?
QQQ is an Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) that is designed to track an index (the Nasdaq-100). This means it combines the features of an index fund (tracking a market benchmark) with the trading flexibility of a stock (can be bought and sold throughout the day).
5. How can I buy QQQ in Canada?
You can buy QQQ in Canada through a brokerage account that offers access to U.S. stock exchanges, such as Questrade, Wealthsimple Trade, or the brokerage arms of major Canadian banks. Since QQQ is priced in U.S. dollars, your brokerage will handle the currency conversion from CAD to USD.
6. What is Warren Buffett's favorite ETF?
Warren Buffett recommends that most individual investors buy a low-cost S&P 500 index fund or ETF. He believes this is the most effective way to own a broad cross-section of American business. He doesn't name a specific ticker, but funds like VOO (Vanguard S&P 500 ETF) and SPY (SPDR S&P 500 ETF) fit his recommendation.
7. Why does Dave Ramsey say not to invest in ETFs?
This is a common misconception. Dave Ramsey is not strictly against ETFs; he is against a lack of diversification. He worries that some ETFs, especially sector-specific ones like QQQ, can lead investors to be too concentrated in one area. His preferred strategy involves a diversified portfolio of four different types of actively managed mutual funds.
8. What is a good ETF for beginners?
A great ETF for beginners is a broad-market, low-cost index fund like the Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO) or the iShares CORE S&P 500 ETF (IVV). These funds provide instant diversification by investing in 500 of the largest U.S. companies, making them an excellent core holding for a new portfolio.
9. Why is an ETF not a good investment for some people?
An ETF might not be a good investment if an investor chooses one that doesn't align with their risk tolerance or goals. For example, highly volatile leveraged or thematic ETFs can lead to significant losses. For others, the temptation to trade ETFs like stocks can lead to poor, emotion-driven decisions compared to the disciplined, long-term approach often associated with mutual funds.
10. What is the 4% rule for ETFs?
The 4% rule is a retirement withdrawal strategy, not a rule specific to ETFs. It suggests that a retiree can withdraw 4% of their portfolio's value in the first year of retirement and then adjust that amount for inflation in subsequent years. This rule can be applied to a retirement portfolio composed of ETFs, stocks, and bonds to help ensure the money lasts for 30 years or more.
At Everyday Next, we're dedicated to providing you with clear, actionable insights to help you navigate the worlds of finance, technology, and personal growth. Whether you're building your first portfolio or looking for the next big idea, our goal is to empower your journey. For more guides and analysis, visit us at https://everydaynext.com.













